Mission
UNITAR’s Role
The United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR), through its Division for People and Social Inclusion, is responsible for the lead, oversight, coordination, and support of the Network, ensuring that all activities align with the principles and regulations of the United Nations, the UNITAR Statute, and its Strategic Framework, as well as the Agenda 2030 and the Sustainable Development Goals. Furthermore, UNITAR certifies and endorses the training programmes developed by the CIFAL Centres, ensuring they meet the highest standards of excellence.
UNITAR remains actively engaged with the CIFAL Global Network by providing continuous monitoring and support. This includes offering advice and expertise on learning methodologies, thematic areas, and operational strategies. Through this sustained partnership, UNITAR helps to ensure that the CIFAL Centres are well-equipped to deliver impactful and meaningful training programmes around the world.
About the CIFAL Global Network
CIFAL stands for “Centre International de Formation des Autorités et Leaders” (in French), and “Centro Internacional de Formación para Autoridades y Líderes” (in Spanish).
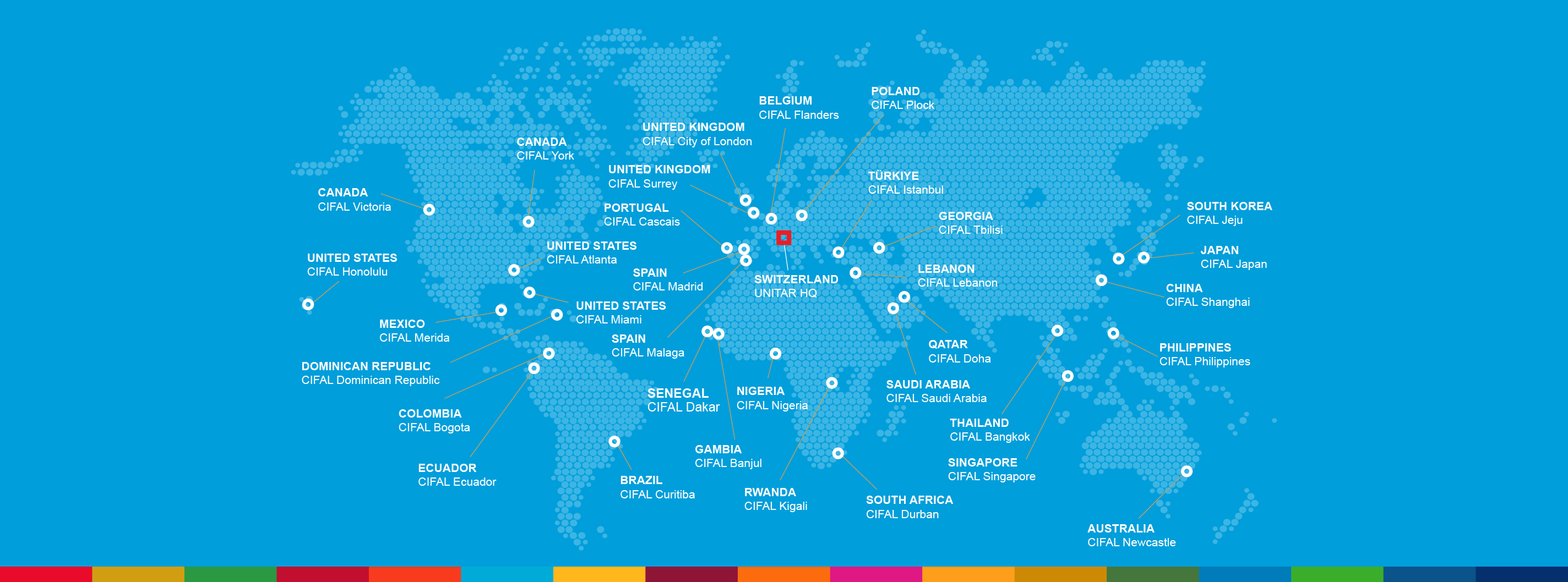
The CIFAL Global Network, as for 2024, is composed by 35 International Training Centres for Authorities and Leaders, all coordinated by UNITAR’s Social Development Programme. Strategically located across Asia, Oceania, Africa, Europe, the Americas, and the Caribbean, these centres are designed to ensure a truly global outreach. Each CIFAL centre serves as a hub for innovation and knowledge exchange, offering high-impact training that brings together government officials, the private sector, academia and civil society. By fostering collaboration across sectors and regions, the CIFAL centres are instrumental in promoting sustainable development and empowering local leaders to address global challenges.
The central purpose of the CIFAL training programs is to develop and strengthen human capacities to better respond to development challenges and to facilitate City-to-City (C2C) partnerships.
Through knowledge management methodologies, CIFALs provide networking opportunities that lead to collaboration, facilitation of peer-to-peer learning and exchange of best practices.
The CIFAL Global Network was launched in 2003 and since its inception has had a significant impact on reaching beneficiaries worldwide. In 2023 alone, the network reached 97,407 beneficiaries through 422 events.
Thematic Areas
















CIFAL Approach
Target Audience
The primary beneficiaries of CIFAL programs are government officials from developing countries who are committed to adopting strategic approaches to development. Other key participants include:
- Public Officials: From national, sub-national, and local governments.
- Academics: Scholars and researchers focused on sustainable development.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and Community-Based Organizations (CBOs): Those engaged in community development and advocacy.
- Private Sector Representatives: Business leaders and corporate entities involved in sustainability initiatives.
- International Organizations: Entities supporting global development efforts.
The CIFAL Global Network, under the guidance of UNITAR, continues to play a pivotal role in empowering individuals and communities to meet development challenges head-on. Through its comprehensive training programs and collaborative platform, CIFAL contributes to building a more sustainable and inclusive world.
Sustainable Development Goals
The CIFAL Global Network also plays a vital role in promoting awareness of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, including its 17 Goals and 169 Targets, through targeted training initiatives. Its significant growth in the provision and reach of training services highlights both the expansion of the Network and the persistent demand for capacity-building at local and subnational levels. Both UNITAR and the CIFAL Global Network are deeply committed to contributing meaningfully and impactfully to the successful implementation of this global Agenda.


SDG 1 (No Poverty)
Eradicate extreme poverty, defined as living on less than $1.25 a day. Reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women, and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions. Implement social protection systems for all.

SDG 2 (Zero Hunger)
End hunger and ensure access for all people to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food all year round. Double the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers. Ensure the sustainability of food production systems.

SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being)
Reduce the global maternal mortality ratio and neonatal mortality. End the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and other communicable diseases. Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services.

SDG 4 (Quality Education)
Ensure that all children complete free, equitable, and quality primary and secondary education. Increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills for employment. Eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access.

SDG 5 (Gender Equality)
End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls. Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls. Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership.

SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation)
Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. Improve water quality by reducing pollution. Increase water-use efficiency across all sectors.

SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy)
Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services. Substantially increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. Improve energy efficiency.

SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth)
Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances. Achieve higher levels of economic productivity. Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation.

SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure)
Develop quality, reliable, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure. Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization. Enhance scientific research and upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors.

SDG 10 (Reduced Inequality)
Achieve and sustain income growth of the bottom 40% of the population at a rate higher than the national average. Promote the social, economic, and political inclusion of all. Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome.

SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities)
Ensure access for all to adequate, safe, and affordable housing and basic services. Provide access to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transport systems. Enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization.

SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production)
Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. Halve per capita global food waste. Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse.

SDG 13 (Climate Action)
Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters. Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning. Improve education, awareness, and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation.

SDG 14 (Life Below Water)
Prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution. Sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems. Regulate harvesting and end overfishing.

SDG 15 (Life on Land)
Ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems. Combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil. Halt biodiversity loss.

SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions)
Significantly reduce all forms of violence. Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all. Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms.

SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals)
Strengthen domestic resource mobilization. Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory, and equitable multilateral trading system. Enhance global macroeconomic stability.






